推荐列表
Netty(网络-java)
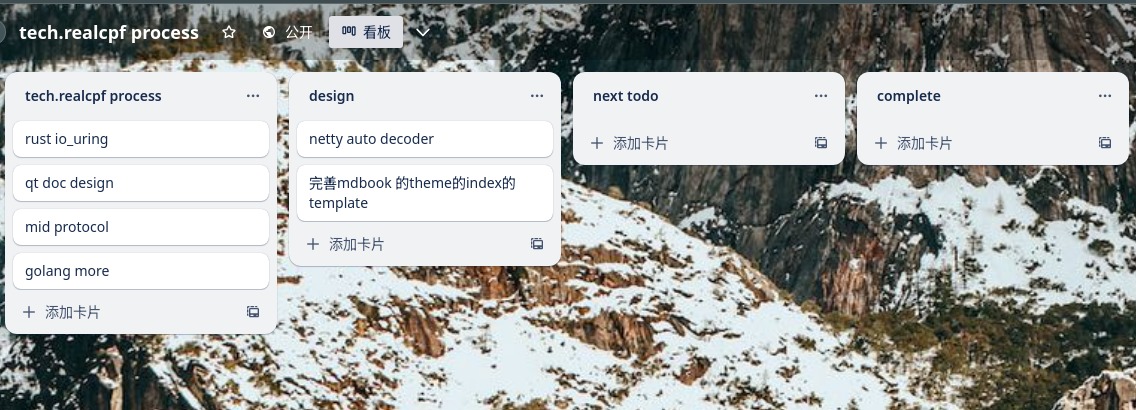
Netty is an asynchronous event-driven network application framework for rapid development of maintainable high performance protocol servers & clients.
EventLoopGroup
EventLoopGroup 如名是EventLoop的Group 用于管理EventLoop。EventLoopGroup可以理解为一个线程池,其中的线程(EventLoop)负责处理事件和任务。
selectable
// single thread pool
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
// loop one
NioEventLoop loop = (NioEventLoop) group.next();
try {
Channel channel = new NioServerSocketChannel();
loop.register(channel).syncUninterruptibly();
channel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(0)).syncUninterruptibly();
// config selector
SocketChannel selectableChannel = SocketChannel.open();
selectableChannel.configureBlocking(false);
selectableChannel.connect(channel.localAddress());
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// register key
loop.register(selectableChannel, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT, new NioTask<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void channelReady(SocketChannel ch, SelectionKey key) {
latch.countDown();
}
@Override
public void channelUnregistered(SocketChannel ch, Throwable cause) {
}
});
latch.await();
selectableChannel.close();
channel.close().syncUninterruptibly();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
full param group and new task queue
final AtomicBoolean called = new AtomicBoolean();
NioEventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(
1, // 线程数
new ThreadPerTaskExecutor(new DefaultThreadFactory(NioEventLoopGroup.class)), // Executor
DefaultEventExecutorChooserFactory.INSTANCE, SelectorProvider.provider(), // selector
DefaultSelectStrategyFactory.INSTANCE, RejectedExecutionHandlers.reject(), // 拒绝策略
new EventLoopTaskQueueFactory() { // task queue factory
@Override
public Queue<Runnable> newTaskQueue(int maxCapacity) {
called.set(true);
return new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(maxCapacity);
}
});
final NioEventLoop loop = (NioEventLoop) group.next();
try {
loop.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// do some
}
}).syncUninterruptibly();
assert true == called.get();
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
delay await cancel
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup(1);
final EventLoop el = group.next();
// schedule
Future<?> future = el.schedule(() -> {
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}, Long.MAX_VALUE, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// await
assert false == future.awaitUninterruptibly(100);
// cancel
assert true == future.cancel(true);
group.shutdownGracefully();
Channel
Channel是网络传输中的实体,它代表了一个开放的连接,可以进行数据的读写操作。
channel init
final String A = "a";
final String B = "B";
// inbound handler
ChannelHandler handler = new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter() {
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
ctx.fireChannelRead(A);
ctx.fireChannelRead(B);
}
};
// channel
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(
new ChannelInitializer<Channel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(Channel channel) throws Exception {
channel.pipeline().addLast(handler);
}
}
);
assert handler == channel.pipeline().firstContext().handler();
assert true == channel.writeInbound("C");
assert true == channel.finish();
assert A.equals(channel.readInbound());
assert B.equals(channel.readInbound());
Scheduling
EmbeddedChannel ch = new EmbeddedChannel(new ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter());
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(2);
// future
Future future = ch.eventLoop().schedule(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("future");
latch.countDown();
}
}, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
// 监听future完成
future.addListener(new FutureListener() {
@Override
public void operationComplete(Future future) throws Exception {
System.out.println("operationComplete");
latch.countDown();
}
});
// run pending schedule task
long next = ch.runScheduledPendingTasks();
System.out.println(next);
assert next > 0;
TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.sleep(TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(next) + 66);
assert ch.runScheduledPendingTasks() == -1;
System.out.println(next);
latch.await();
ByteBuf
ByteBuf作为java NIO中ByteBuffer的Netty版,其语义与ByteBuffer相同,只是操作方式更加丰富
基本操作
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer(128);
List<Object> objects = new LinkedList<>();
objects.add(buf.capacity());
objects.add(buf.isReadable());
objects.add(buf.isDirect());
objects.add(buf.isReadable());
objects.forEach(System.out::println);
buf.writeByte('a');
buf.writeByte('b');
buf.writeByte('c');
System.out.println(buf.writerIndex());
System.out.println(buf.readerIndex());
System.out.println(buf.readableBytes());
assert 'a' == buf.readByte();
assert 'b' == buf.readByte();
assert 'c' == buf.readByte();
buf.readerIndex(0);
buf.slice(0,3);
buf.release();
ByteProcess
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.buffer(128);
buf.writeCharSequence("abc d \re \n f \b c! ?", StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
int i = 0;
int last = 0;
while (-1 != (i = buf.forEachByte(b -> b != 'c'))) {
if (i > last) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[i - last];
buf.readBytes(buf,i,last);
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
buf.readerIndex(i + 1);
}
last = i;
}
buf.readerIndex(0);
buf.forEachByte(ByteProcessor.FIND_LF);
UnPooled
byte[] bytes1 = "hello".getBytes(StandardCharsets.US_ASCII);
byte[] space = " ".getBytes(StandardCharsets.US_ASCII);
byte[] bytes2 = "world".getBytes(StandardCharsets.US_ASCII);
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(bytes1,space,bytes2);
int len = bytes1.length + bytes2.length + space.length;
byte[] helloWorld = new byte[len];
buf.readBytes(helloWorld,0,len);
System.out.println(new String(helloWorld));
buf.readerIndex(0);
ByteBuf buf3_14 = Unpooled.copyFloat(3.14f);
ByteBuf buf2 = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(buf,buf3_14);
buf2.readerIndex(len);
assert "3.14" == buf2.readFloat() + "";
}
ByteToMessage,MessageToByte,MessageToMessage
串行的数据流的编码解码
ByteToMessage
public static void main(String[] args) {
testM2M();
}
private static void testBase(){
// xxxx\r\nxxx\r\n
ByteToMessageDecoder decoder = new ByteToMessageDecoder() {
@Override
protected void decode(
ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, // 上下文
ByteBuf byteBuf, // 数据buffer
List<Object> list // 传给下一层的对象
) throws Exception {
while (byteBuf.isReadable()) {
int crlfIndex = byteBuf.forEachByte(ByteProcessor.FIND_CRLF);
if (crlfIndex == -1) {
break;
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[crlfIndex - byteBuf.readerIndex()];
byteBuf.readBytes(bytes,0,crlfIndex - byteBuf.readerIndex());
byteBuf.readerIndex(crlfIndex);
byteBuf.readShort();
list.add(new String(bytes));
}
}
};
MessageToMessage
ByteToMessageDecoder decoder = new ByteToMessageDecoder() {
@Override
protected void decode(
ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, // 上下文
ByteBuf byteBuf, // 数据buffer
List<Object> list // 传给下一层的对象
) throws Exception {
while (byteBuf.isReadable()) {
int crlfIndex = byteBuf.forEachByte(ByteProcessor.FIND_CRLF);
if (crlfIndex == -1) {
break;
}
byte[] bytes = new byte[crlfIndex - byteBuf.readerIndex()];
byteBuf.readBytes(bytes,0,crlfIndex - byteBuf.readerIndex());
byteBuf.readerIndex(crlfIndex);
byteBuf.readShort();
list.add(new String(bytes));
}
}
};
MessageToMessageDecoder decoderM2M = new MessageToMessageDecoder() {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, Object o, List list) throws Exception {
if (o instanceof String) {
list.add(String.format("[%s]",o));
}
}
};
EmbeddedChannel channel = new EmbeddedChannel(decoder);
channel.pipeline().addLast(decoderM2M);
channel.writeInbound(Unpooled.wrappedBuffer("hello\r\nworld\r\n".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8)));
assert "[hello]" == (String) channel.readInbound();
assert "[world]" == (String) channel.readInbound();
Replaying
// replaying 可以用在一个Message再传输时不在同一时间到达的情况
ReplayingDecoder<Void> replayingDecoder = new ReplayingDecoder<Void>() {
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext channelHandlerContext, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
ByteBuf msg = in.readBytes(in.bytesBefore((byte) '\n'));
out.add(msg);
in.skipBytes(1);
}
};
EmbeddedChannel ch = new EmbeddedChannel(replayingDecoder);
ch.writeInbound(Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(new byte[]{'A'}));
assert Objects.isNull(ch.readInbound());
ch.writeInbound(Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(new byte[]{'B'}));
assert Objects.isNull(ch.readInbound());
ch.writeInbound(Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(new byte[]{'C'}));
assert Objects.isNull(ch.readInbound());
// 直到 \n 传到才完成一个Message的decode
ch.writeInbound(Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(new byte[]{'\n'}));
ByteBuf buf = Unpooled.wrappedBuffer(new byte[] { 'A', 'B', 'C' });
ByteBuf buf2 = ch.readInbound();
assert buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8).equals(buf2.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
buf2.release();
buf.release();
ch.finish();
Codec
// codec 同时有decode和encode
ByteToMessageCodec<Integer> codec = new ByteToMessageCodec<Integer>() {
@Override
protected void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Integer msg, ByteBuf out) {
out.writeInt(msg);
}
@Override
protected void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) {
if (in.readableBytes() >= 4) {
out.add(in.readInt());
}
}
};
ByteBuf buffer = Unpooled.buffer();
buffer.writeInt(1);
buffer.writeByte('0');
EmbeddedChannel ch = new EmbeddedChannel(codec);
assert ch.writeInbound(buffer);
ch.pipeline().remove(codec);
assert ch.finish();
assert Integer.compare(1, (Integer) ch.readInbound()) == 0;
}
客制化协议解决方案 - Netty
对于一些非常规的数据传递,目前一般的做法是将数据先行序列化然后通过成熟的协议传输
诚然这样是成熟的、简单的、低设计成本的,但如果对于一些行业可以直接将其数据格式做成应用层协议,继而直接传输
想来减少了两次转换也能提升不少品质,而且对于一些传统的接收数据后的逻辑操作在netty上也可以通过增加handler的方式
尽可能多的完成数据处理的相关操作以提供尽量可用的业务对象用于其他计算

客制化协议解决方案
基于netty实现可以通过配置文件生成pipline和decode、encode的逻辑
?
实现设计 by Netty
总结几种常见协议在netty上的核心实现逻辑
redis
- decode逻辑总结

- 抽取公共部分

- 概念代码
while (true) {
if (!in.isReadable()) {
break;
}
byte first = in.readByte();
switch (first) {
case '*':
case '+':
case '-':
case ':': {
ByteBuf buf = findSliceRead(in,processor);
if (null != buf) {
out.add(buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
}
break;
case '$': {
ByteBuf buf = findSliceRead(in,processor);
lastLen = Integer.parseInt(buf.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
out.add(lastLen);
ByteBuf buf1 = sliceRead(in,lastLen);
out.add(buf1.toString(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
Jdbc(DB Driver - java)
jdbc - db in java的基石
Jdbc - SPI Driver
详见 java.sql.Driver;java.sql.DriverManager;
SPI demo
// the driver interface
public interface MyDriver {
String format();
String who();
}
// the driver of my impl
public class TheDriver implements MyDriver{
@Override
public String format() {
return "mydriver://realcpf";
}
@Override
public String who() {
return "realcpf";
}
}
// SPI config file
// src\main\resources\META-INF\services\tech.realcpf.jdbc.MyDriver -> tech.realcpf.jdbc.TheDriver
加载方式
class MyDriverManager {
private volatile boolean initFlag = false;
public void init() {
if (initFlag) {
return;
}
ServiceLoader<MyDriver> serviceLoader = ServiceLoader.load(MyDriver.class);
Iterator<MyDriver> driverIterator = serviceLoader.iterator();
while (driverIterator.hasNext()) {
MyDriver driver = driverIterator.next();
System.out.println(driver.who() + ":" + driver.format());
}
}
}
Jdbc - Some APIs
some api
表结构、列信息获取
try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("");
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("select * from table where 1=2")) {
final ResultSetMetaData metaData = preparedStatement.getMetaData();
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
IntStream.rangeClosed(1, columnCount).forEach(i -> {
try {
String colName = metaData.getColumnName(i);
String colTypeName = metaData.getColumnTypeName(i);
int colType = metaData.getColumnType(i);
metaData.getPrecision(i);
metaData.getScale(i);
metaData.isAutoIncrement(i);
metaData.isDefinitelyWritable(i);
metaData.isReadOnly(i);
metaData.isWritable(i);
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
} catch (SQLException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
查询
try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("");
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement("");
ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery()) {
int colCount = rs.getMetaData().getColumnCount();
while (rs.next()) {
for (int i = 0; i < colCount; i++) {
final int type = rs.getMetaData().getColumnType(i);
switch (type) {
case Types.VARBINARY: {
}
break;
case Types.INTEGER: {
}
break;
default: {
}
break;
}
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
事务
Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("");
try (connection;
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement("");) {
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
connection.setTransactionIsolation(Connection.TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ);
statement.executeUpdate();
connection.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
connection.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
connection.setAutoCommit(true);
}
DataX(离线同步-java)
DataX is a batch sync framework also an efficient and concise solution

DataX Core transport
reader -> queue -> writer
这是一个极其简化的代码示例 reader -> queue -> writer
// demo Exchanger
private class DemoExchanger {
// 用于从reader到writer传输record的队列
private final BlockingQueue<Object> queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(128);
// writer
private final Runnable writer = new Runnable() {
private final int batchSize = 4;
// record接收器
private Object rev(){
return doPoll();
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("writer:");
Object o;
// 写入批
List<Object> batch = new ArrayList<>(batchSize);
while (null != (o = rev())) {
batch.add(o);
if (batch.size() >= batchSize) {
batch.forEach(System.out::println);
batch.clear();
}
}
if (batch.size() >= batchSize) {
batch.forEach(System.out::println);
batch.clear();
}
}
};
// reader
private final Runnable reader = new Runnable() {
// record 发送器
private void send(Object o){
doPush(o);
}
@Override
public void run() {
Random random = new Random();
int i = 0;
System.out.println("reader:");
// 生成数据
while (true) {
if (i > 12) {
i = 0;
}
send(random.nextLong());
i++;
}
}
};
/**
* reader push
* @param o record
*/
private void doPush(Object o) {
try {
queue.put(o);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
/**
* writer poll
* @return
*/
private Object doPoll() {
try {
return queue.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new IllegalStateException(e);
}
}
public void test(){
Thread writerThread = new Thread(writer);
Thread readerThread = new Thread(reader);
//先启动writer 再启动reader
writerThread.start();
readerThread.start();
}
}
Job Reader
https://github.com/alibaba/DataX/blob/master/dataxPluginDev.md

关于分片这里有一个可供参考的计算方法ReaderSplitUtil
public class DemoReader extends Reader{
// job
// 需要实现的方法有
// split(int i) 分片方法
// init() 初始化
// destroy() 销毁
public static class Job extends Reader.Job{
private Configuration originalConfig;
@Override
public List<Configuration> split(int i) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void init() {
this.originalConfig = this.getPluginJobConf();
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
// Task
// 需要实现的方法
// startRead(RecordSender recordSender) reader的开始方法
// 这里会生成Record 送往Writer
// init() 初始化
// destroy() 销毁
public static class Task extends Reader.Task {
private Configuration readerSliceConfig;
@Override
public void startRead(RecordSender recordSender) {
Record record = recordSender.createRecord();
//
Column column = new StringColumn("");
record.addColumn(column);
recordSender.sendToWriter(record);
}
@Override
public void init() {
this.readerSliceConfig = super.getPeerPluginJobConf();
// init
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
}
Job Writer
https://github.com/alibaba/DataX/blob/master/dataxPluginDev.md
public class DemoWriter extends Writer {
// init split destroy
public static class Job extends Writer.Job{
private Configuration originalConfig;
@Override
public List<Configuration> split(int i) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void init() {
this.originalConfig = this.getPluginJobConf();
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
// startWrite init destroy
public static class Task extends Writer.Task {
private Configuration writerSliceConfig;
@Override
public void startWrite(RecordReceiver recordReceiver) {
Record record = recordReceiver.getFromReader();
String s = record.getColumn(0).asString();
}
@Override
public void init() {
this.writerSliceConfig = super.getPluginJobConf();
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
}
}
Spring Base Utils
Spring IoC and Bean
The org.springframework.beans and org.springframework.context packages are the basis for Spring Framework’s IoC container. The BeanFactory interface provides an advanced configuration mechanism capable of managing any type of object. ApplicationContext is a sub-interface of BeanFactory. It adds:
- Easier integration with Spring’s AOP features
- Message resource handling (for use in internationalization)
- Event publication
- Application-layer specific contexts such as the WebApplicationContext for use in web applications.
Create Config Get Beans
ApplicationContext context1 = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContex("services.xml");
ApplicationContext context2 = new GenericGroovyApplicationContext("services.groovy");
ApplicationContext context3 = FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("")
private static void testBean1(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("services.xml");
// getBean
DemoEntity entity1 = context.getBean("entity1", DemoEntity.class);
System.out.println(entity1);
DemoEntity entityAlias = context.getBean("entityAlias",DemoEntity.class);
System.out.println(entityAlias);
XML config attrs
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!-- factory-method -> public static factory method -->
<bean id="entity2" class="tech.realcpf.spring.dto.DemoEntity" factory-method="createInstance">
<property name="name" value="jiacheng.liu"/>
<property name="age" value="25"/>
</bean>
<!-- use xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"-->
<bean id="entity3" class="tech.realcpf.spring.dto.DemoEntity"
destroy-method="destroy"
p:name="jc.liu"
p:age="89">
<!-- additional collaborators and configuration for this bean go here -->
</bean>
<!-- constructor-arg -->
<bean id="entity1" class="tech.realcpf.spring.dto.DemoEntity">
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="by constructor" name="name" index="0"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.Integer" value="123" name="age" index="1"></constructor-arg>
</bean>
<alias name="entity1" alias="entityAlias"></alias>
<!-- depends-on other beans -->
<bean id="beanOne" class="ExampleBean" depends-on="manager"/>
<!-- <bean id="manager" class="ManagerBean" />-->
<!-- lazy-init -->
<bean id="lazy" class="com.something.ExpensiveToCreateBean" lazy-init="true"/>
<!-- <bean name="not.lazy" class="com.something.AnotherBean"/>-->
<!-- init method -->
<bean id="exampleInitBean" class="examples.ExampleBean" init-method="init"/>
<!-- scope -->
<bean id="exampleInitBean" class="examples.ExampleBean" scope="prototype"/>
</beans>
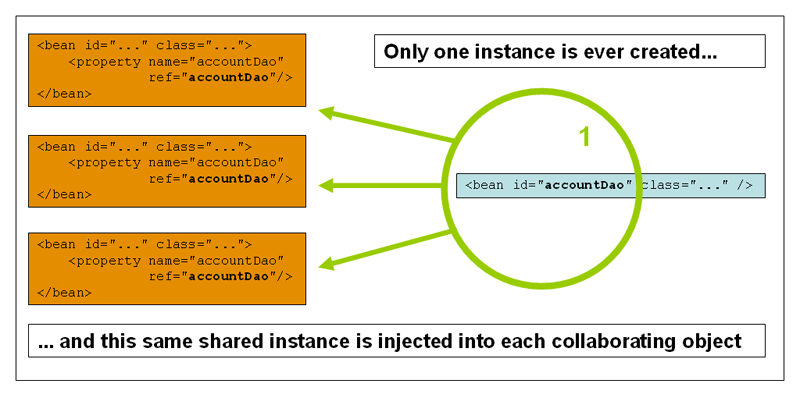
BeanPostProcessor
private static final BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor = new BeanPostProcessor() {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("Bean '" + beanName + "' created : " + bean.toString());
return BeanPostProcessor.super.postProcessAfterInitialization(bean, beanName);
}
};
// PropertyOverrideConfigurer
// PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
private static final BeanFactoryPostProcessor beanFactoryPostProcessor = new BeanFactoryPostProcessor() {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
}
};
Spring SPI
通过 resources/META-INF/spring.factories 作为SPI的配置文件
内容如下:
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
tech.realcpf.spring.DemoApplicationContextInitializer
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
tech.realcpf.spring.DemoApplicationListener
如果用spring-boot,再spring-boot3之后配置文件改成
resources/META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports 作为SPI的配置文件
内容则是一个类一行
其中 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration 是Interface名
Spring Aop
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/core/aop-api/pointcuts.html
Proxy - ProxyFactoryBean
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aopdemo.xml");
IDemoModel model = (IDemoModel) context.getBean("demoModelProxy");
System.out.println(model.hello("jc.liu"));
<bean id="demoModelProxy"
class="org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactoryBean">
<property name="proxyInterfaces">
<list>
<value>tech.realcpf.spring.aop.IDemoModel</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="target" ref="demoModelImpl">
</property>
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>demoModelArgs</value> <!-- impl MethodBeforeAdvice -->
<value>demoModelReturn</value> <!-- impl AfterReturningAdvice -->
</list>
</property>
</bean>
Auto Proxy - BeanNameAutoProxyCreator
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("aopdemo.xml");
IDemoModel demoModel = context.getBean(IDemoModel.class);
System.out.println(demoModel.hello("jc.liu"));
<bean class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator">
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>demoModelArgs</value>
<value>demoModelReturn</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- for auto match-->
<property name="beanNames" value="*Model"></property>
</bean>
Aspectj
// call before
@Before("tech.realcpf.spring.aop.aj.SystemArchitecture.service()")
public void callBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
System.out.println("Before : " + Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
// call after
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "tech.realcpf.spring.aop.aj.SystemArchitecture.service()",
returning = "result")
public void logResult(Object result) {
System.out.println("after :" + result);
}
@Pointcut("execution(* tech.realcpf.spring.aop.aj..*(..))")
public void service() {}
<!-- enable aspectj -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
Spring EL
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/reference/core/expressions/evaluation.html
更多的语法语义
static class Simple {
public List<Boolean> booleans = new ArrayList<>();
}
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression("'Hello World'.concat('!')");
String message = (String) exp.getValue();
System.out.println(message);
System.out.println(
parser.parseExpression("'hello'.bytes.length").getValue()
);
Simple simple = new Simple();
simple.booleans.add(false);
EvaluationContext context = SimpleEvaluationContext.forReadOnlyDataBinding().build();
parser.parseExpression("booleans[0]")
.setValue(context,simple,"true");
assert simple.booleans.get(0);
Kafka Stream Calc and Message Queue
生产者 -> Stream Processor -> 消费者
Kafka 设计思想
https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#design
Poll or Push
Message Format
log 文件
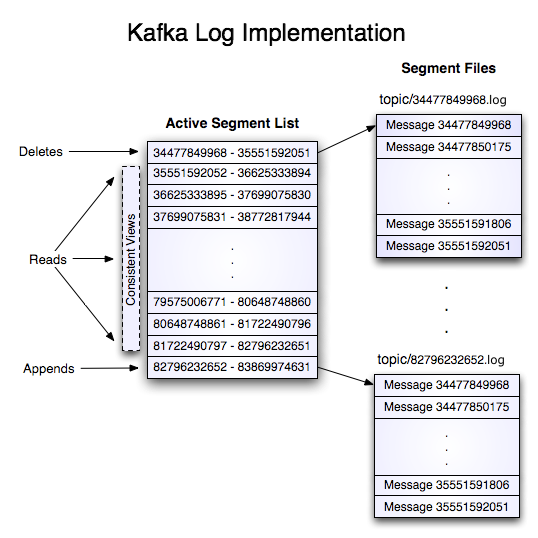
Kafka Admin
查看Topic
/*
bin/kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --describe
*/
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put(AdminClientConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "localhost:9092");
try (Admin admin = Admin.create(props)) {
ListTopicsResult result = admin.listTopics();
result.namesToListings().whenComplete(((stringTopicListingMap, throwable) -> {
for (Map.Entry<String, TopicListing> entity:stringTopicListingMap.entrySet()) {
System.out.println(entity.getKey());
System.out.println(entity.getValue().topicId());
System.out.println(entity.getValue().name());
System.out.println(entity.getValue());
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
}
}));
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
创建Topic
/**
* bin/kafka-topics.sh --create \
* --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
* --replication-factor 1 \
* --partitions 1 \
* --topic streams-wordcount-output \
* --config cleanup.policy=compact
*/
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put(AdminClientConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "localhost:9092");
try (Admin admin = Admin.create(props)) {
String topicName = "create-topic-with-java";
int partitions = 1;
short replicationFactor = 1;
// Create a compacted topic
CreateTopicsResult result = admin.createTopics(Collections.singleton(
new NewTopic(topicName, partitions, replicationFactor)
.configs(Collections.singletonMap(TopicConfig.CLEANUP_POLICY_CONFIG,
TopicConfig.CLEANUP_POLICY_COMPACT))));
// Call values() to get the result for a specific topic
KafkaFuture<Void> future = result.values().get(topicName);
// Call get() to block until the topic creation is complete or has failed
// if creation failed the ExecutionException wraps the underlying cause.
future.get();
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
删除Topic
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put(AdminClientConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "localhost:9092");
try (Admin admin = Admin.create(props)) {
TopicCollection topicCollection = TopicCollection.ofTopicNames(
Collections.singleton("create-topic-with-java"));
DeleteTopicsResult result = admin.deleteTopics(topicCollection);
result.all().whenComplete((r,t) ->{
if (t != null) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("delete done!");
});
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
Kafka Consumer
基本消费者代码
// 配置属性
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092");
props.setProperty("group.id", "test");
props.setProperty("enable.auto.commit", "true");
props.setProperty("auto.commit.interval.ms", "1000");
props.setProperty("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
props.setProperty("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
try(KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(props)) {
// 订阅
consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList("quickstart-events"));
while (true) {
// 拉取
ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(100));
for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records)
System.out.printf("offset = %d, key = %s, value = %s%n", record.offset(), record.key(), record.value());
}
}
更详细的消费控制
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092");
props.setProperty("group.id", "test");
props.setProperty("enable.auto.commit", "false");
props.setProperty("key.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
props.setProperty("value.deserializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer");
KafkaConsumer<String, String> consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(props);
consumer.subscribe(Arrays.asList("quickstart-events"), new ConsumerRebalanceListener() {
@Override
public void onPartitionsRevoked(Collection<TopicPartition> collection) {
for (TopicPartition part:collection) {
// 获取offset 可以自行处理
Long currOffset = consumer.position(part);
// we can save the offset in own db
}
}
@Override
public void onPartitionsAssigned(Collection<TopicPartition> collection) {
// consumer.seekToBeginning(collection);
for (TopicPartition part:collection) {
// get offset from own db
// 可以从自己的系统取得offset 以达将offset与业务系统进行关联
Long currOffset = 0L;
consumer.seek(part,currOffset);
}
}
});
// 按照批去
final int minBatchSize = 10;
List<ConsumerRecord<String, String>> buffer = new ArrayList<>();
while (true) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(100));
for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) {
buffer.add(record);
}
if (buffer.size() >= minBatchSize) {
printThis(buffer);
// 手动提交
consumer.commitAsync();
buffer.clear();
}
}
// 指定分区
String topic = "foo";
TopicPartition partition0 = new TopicPartition(topic, 0);
TopicPartition partition1 = new TopicPartition(topic, 1);
consumer.assign(Arrays.asList(partition0, partition1));
Kafka Productor
基本生产者
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092");
props.put("linger.ms", 1);
props.put("key.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
props.put("value.serializer", "org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer");
try(Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props)){
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<String, String>("quickstart-events", Integer.toString(i), Integer.toString(i)));
}
producer.flush();
}
事务
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("bootstrap.servers", "localhost:9092");
props.put("transactional.id", "my-transactional-id");
try(Producer<String, String> producer = new KafkaProducer<>(props, new StringSerializer(), new StringSerializer())) {
producer.initTransactions();
producer.beginTransaction();
for (int i = 0;i<10;i++){
producer.send(new ProducerRecord<>("quickstart-events",Integer.toString(i),Integer.toString(i)));
}
producer.commitTransaction();
} catch (ProducerFencedException | OutOfOrderSequenceException | AuthorizationException e) {
} catch (KafkaException e) {
}
Kafka Stream
Stream 基本结构
// 属性配置
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put(StreamsConfig.APPLICATION_ID_CONFIG, "streams-wordcount");
props.put(StreamsConfig.BOOTSTRAP_SERVERS_CONFIG, "localhost:9092");
props.put(StreamsConfig.DEFAULT_KEY_SERDE_CLASS_CONFIG, Serdes.String().getClass());
props.put(StreamsConfig.DEFAULT_VALUE_SERDE_CLASS_CONFIG, Serdes.String().getClass());
// stream 构建器
final StreamsBuilder builder = new StreamsBuilder();
// builder.stream("Source-Topic").xxx.xxx.to("Sink-Topic")
builder.<String, String>stream("streams-plaintext-input")
.flatMapValues(value -> Arrays.asList(value.toLowerCase(Locale.getDefault()).split("\\W+")))
.groupBy((key, value) -> value)
.count(Materialized.<String, Long, KeyValueStore<Bytes, byte[]>>as("counts-store"))
.toStream()
.to("streams-wordcount-output", Produced.with(Serdes.String(), Serdes.Long()));
final Topology topology = builder.build();
final KafkaStreams streams = new KafkaStreams(topology, props);
final CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
// attach shutdown handler to catch control-c
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread("streams-shutdown-hook") {
@Override
public void run() {
streams.close();
latch.countDown();
}
});
try {
streams.start();
latch.await();
} catch (Throwable e) {
System.exit(1);
}
System.exit(0);
}
Processor
import org.apache.kafka.streams.KeyValue;
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.PunctuationType;
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.api.Processor;
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.api.ProcessorContext;
import org.apache.kafka.streams.processor.api.Record;
import org.apache.kafka.streams.state.KeyValueIterator;
import org.apache.kafka.streams.state.KeyValueStore;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Locale;
public class WorldCountProcessor implements Processor<String,String,String,String> {
private KeyValueStore<String,Integer> keyValueStore;
@Override
public void process(Record<String,String> record) {
final String[] words =
record.value().toUpperCase(Locale.ROOT).split("\\W+");
for (final String word:words) {
final Integer oldValue = keyValueStore.get(word);
if (oldValue == null) {
keyValueStore.put(word,1);
}else {
keyValueStore.put(word,oldValue + 1);
}
}
}
@Override
public void close() {
}
@Override
public void init(ProcessorContext context) {
context.schedule(Duration.ofSeconds(1),
PunctuationType.STREAM_TIME,
timestamp ->{
try(final KeyValueIterator<String,Integer> iter = keyValueStore.all()) {
while (iter.hasNext()) {
final KeyValue<String,Integer> entry = iter.next();
context.forward(new Record(entry.key,entry.value.toString(),timestamp));
}
}
});
keyValueStore = context.getStateStore("Counts");
}
}
Topology use Processor
Stores
.keyValueStoreBuilder(
Stores.persistentKeyValueStore("Counts"),
Serdes.String(),
Serdes.Long()
);
builder.addSource("Source","source-topic")
.addProcessor("Processor", () -> new WorldCountProcessor(),"Source")
.addStateStore(countsStoreBuilder,"Process")
.addSink("Sink","sink-topic","Process");
}
// kafka test driver
// https://kafka.apache.org/35/documentation/streams/developer-guide/testing
}
Test Driver
Akka (Actor)
https://akka.io/
Akka
基本用法 创建、传递消息
创建
import akka.actor.AbstractActor;
import akka.actor.Props;
import java.time.Duration;
public class DemoRev extends AbstractActor {
public DemoRev(){
// 设置接收消息的超时时间
getContext().setReceiveTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(10));
}
/**
* 用于创建ActorRef
**/
public static Props props(){
return Props.create(DemoRev.class, DemoRev::new);
}
@Override
public Receive createReceive() {
return receiveBuilder()
.match(String.class ,//如果是string类型
r->{
System.out.println("rev :" + r);
getSender().tell("rev done",getSelf());
}).match(Integer.class, // 如果是Interger类型
r->{
getSender().tell("give me more!",getSelf());
}).matchAny(a->{ // 其他
System.out.println("any");
}).build();
}
}
传递消息
ActorSystem system = ActorSystem.create("linux");
// 创建
ActorRef p1 = system.actorOf(DemoRev.props());
ActorRef s1 = system.actorOf(DemoSend.props());
// s1 -> p1
p1.tell("hello",s1);
system.terminate();
Inbox 消息
ActorSystem system = ActorSystem.create("linux");
ActorRef p1 = system.actorOf(DemoRev.props());
final Inbox inbox = Inbox.create(system);
// inbox也是一个actor
inbox.send(p1,"hello");
System.out.println(inbox.receive(Duration.ofSeconds(1)));
system.terminate();
周期性消息
import akka.actor.AbstractActorWithTimers;
import java.time.Duration;
public class DemoTimer extends AbstractActorWithTimers {
private static Object TICK_KEY = "TickKey";
private static final class FirstTick {}
private static final class Tick {}
public DemoTimer(){
// 相当于settimeout
getTimers().startSingleTimer(TICK_KEY,new FirstTick(), Duration.ofMillis(500));
}
@Override
public Receive createReceive() {
return receiveBuilder().match(
FirstTick.class,
message -> {
// 周期执行
getTimers().startPeriodicTimer(TICK_KEY,new Tick(),Duration.ofSeconds(1));
}
).match(Tick.class,message -> {
System.out.println(message);
}).build();
}
}
生命周期
import akka.actor.AbstractActor;
import akka.actor.Props;
public class StartStopActor1 extends AbstractActor {
static Props props() {
return Props.create(StartStopActor1.class, StartStopActor1::new);
}
// 启动hock
@Override
public void preStart() throws Exception {
System.out.printf("start %s \n",getSelf().path().toSerializationFormat());
getContext().actorOf(StartStopActor2.props(),"second");
}
// 停止hock
@Override
public void postStop() throws Exception {
System.out.printf("stop %s \n",getSelf().path().toSerializationFormat());
}
/*
也可以用信号停止
victim.tell(akka.actor.PoisonPill.getInstance(), ActorRef.noSender());
*/
@Override
public Receive createReceive() {
return receiveBuilder()
.matchEquals("stop",s->{
getContext().stop(getSelf());
}).build();
}
}
Receive
// 支持动态改变receive方法
public Receive createReceive() {
return receiveBuilder()
.matchEquals(
"init",
m1 -> {
initializeMe = "Up and running";
getContext()
.become(
receiveBuilder()
.matchEquals(
"U OK?",
m2 -> {
getSender().tell(initializeMe, getSelf());
})
.build());
})
.build();
ask , pipie
import akka.actor.ActorRef;
import akka.actor.ActorSystem;
import scala.Tuple2;
import tech.realcpf.sendrev.DemoRev;
import tech.realcpf.sendrev.DemoSend;
import static akka.pattern.Patterns.ask;
import static akka.pattern.Patterns.pipe;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture;
public class AskDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ActorSystem system = ActorSystem.create("sys");
ActorRef actorA = system.actorOf(DemoRev.props());
ActorRef actorB = system.actorOf(DemoRev.props());
ActorRef actorC = system.actorOf(DemoRev.props());
CompletableFuture<Object> future1 =
ask(actorA,"hi A", Duration.ofMillis(1000)).toCompletableFuture();
CompletableFuture<Object> future2 =
ask(actorB,"hi B", Duration.ofMillis(1000)).toCompletableFuture();
CompletableFuture<Tuple2<String,String>> transformed =
CompletableFuture.allOf(future1,future2)
.thenApply(v->{
String x = (String) future1.join();
String s = (String) future2.join();
return new Tuple2(x,s);
});
pipe(transformed,system.dispatcher()).to(actorC);
system.terminate();
}
}
Akka Route
Akka FSM
Excelize (OOXML Excel)
https://xuri.me/excelize/zh-hans/
Excelize 基本操作
设置单元格的值
f := excelize.NewFile()
defer func() {
if err := f.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
sheetName := "MySheet"
index, err := f.NewSheet(sheetName)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
// 设置指定单元格的值 需要 sheetName 座标
f.SetCellValue(sheetName, "A2", "Hello World")
f.SetCellValue(sheetName, "B2", 100)
f.SetActiveSheet(index)
if err := f.SaveAs("tmp/excelize.xlsx"); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
读取单元格的值
f, err := excelize.OpenFile("tmp/excelize.xlsx")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
defer func() {
if err := f.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
sheetName := "MySheet"
// 读取指定单元格的值 需要 sheetName 座标
cell, err := f.GetCellValue(sheetName, "B2")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
fmt.Println(cell)
// 也可以获取整个sheet的数据
rows, err := f.GetRows(sheetName)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// 便利表格
for _, row := range rows {
for _, colCell := range row {
fmt.Print(colCell, "\t")
}
fmt.Println()
}
根据表格数据创建chart
在Libre Office中创建chart图如下

对应的代码里如下
f := excelize.NewFile()
defer func() {
if err := f.Close(); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
}()
data := [][]interface{}{
{nil, "Apple", "Orange", "Pear"}, {"Small", 2, 3, 3},
{"Normal", 5, 2, 4}, {"Large", 6, 7, 8},
}
index, err := f.NewSheet("DemoSheet")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
f.SetActiveSheet(index)
for idx, row := range data {
// 坐标到单元格名称将 [X, Y] 坐标转换为单元格
cell, err := excelize.CoordinatesToCellName(1, idx+1)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
// 设置一行数据
f.SetSheetRow("DemoSheet", cell, &row)
}
chartSeries := []excelize.ChartSeries{
{
Name: "DemoSheet!$A$2",
Categories: "DemoSheet!$B$1:$D$1", // 和图里对应
Values: "DemoSheet!$B$2:$D$2",
},
{
Name: "DemoSheet!$A$3",
Categories: "DemoSheet!$B$1:$D$1",
Values: "DemoSheet!$B$3:$D$3",
},
{
Name: "DemoSheet!$A$4",
Categories: "DemoSheet!$B$1:$D$1",
Values: "DemoSheet!$B$4:$D$4",
},
}
if err := f.AddChart("DemoSheet", "E1", &excelize.Chart{
Type: excelize.Col3DClustered,
Series: chartSeries,
Title: excelize.ChartTitle{
Name: "My Demo 3D Chart",
},
}); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
if err := f.SaveAs("tmp/abc.xlsx"); err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
Excelize - 代码生成
Excelize的代码设计规整,文档详细,完全可以通过规则生成代码,下面是一个小例子,还会继续完善
Actix \ Actix-Web
Actix-Actor 实现了 Actor模型 同样实现了Actor模型的还有Akka
Actix Actor
Actor
Actor 创建并发送和接收消息
Actor实现、Message实现
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use actix::{Actor, Context, Message, Handler, dev::MessageResponse}; struct MyActor{ count:usize } /// /// Actor impl Actor for MyActor { // 每个actor都有一个context type Context = Context<Self>; } #[derive(Message)] #[rtype(result = "usize")] struct Ping(usize); impl Handler<Ping> for MyActor { type Result = usize; /// /// 接受Ping类型的消息 然后返回usize fn handle(&mut self, msg: Ping, ctx: &mut Self::Context) -> Self::Result { self.count += msg.0; self.count } } }
发送,接收处理
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[actix::test] async fn test1(){ // 开启新的actor并且返回地址也就近似于akka 中的 ActorRef let addr = MyActor { count:10}.start(); // send 然后handler处理返回 let res = addr.send(Ping(10)).await; print!("Res : {}\n",res.unwrap()); let id = System::current().id(); print!("id:{} will stop",id); System::current().stop(); } }
生命周期函数
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { /// /// 生命周期有 /// + Started /// + Running /// + Stopping /// + Stopped /// /// 重写生命周期函数started,stopped impl Actor for MineActor { type Context = Context<Self>; fn started(&mut self, ctx: &mut Self::Context) { println!("started"); } fn stopped(&mut self, ctx: &mut Self::Context) { println!("stopped") } } }
可Response的Message
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { /// /// 为了可以返回Responses 我们为Responses实现MessageResponse impl<A,M> MessageResponse<A,M> for Responses where A:Actor, M:Message<Result = Responses> { fn handle(self, ctx: &mut <A as Actor>::Context, tx: Option<actix::dev::OneshotSender<<M as Message>::Result>>) { if let Some(tx) = tx { tx.send(self); } } } }
Addr , Recipient
Addr 自己用,Recipient 别人用
两个Actor互相发的结构
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use actix::prelude::*; use std::time::Duration; #[derive(Message)] #[rtype(result = "()")] struct Ping { pub id: usize, } struct Game { counter: usize, name: String, // 给其他actor发送 recipient: Recipient<Ping>, } impl Actor for Game { type Context = Context<Game>; } impl Handler<Ping> for Game { type Result = (); fn handle(&mut self, msg: Ping, ctx: &mut Context<Self>) { self.counter += 1; if self.counter > 10 { System::current().stop(); } else { println!("[{0}] Ping received {1}", self.name, msg.id); ctx.run_later(Duration::new(0, 100), move |act, _| { // 给recipient发 在这个例子里就是 另一个Game Actor act.recipient.do_send(Ping { id: msg.id + 1 }); }); } } } }
示例互啄树术
/// /// game 互啄 fn main() { let mut system = System::new(); let addr = system.block_on(async { Game::create(|ctx| { // game1 的 addr let addr = ctx.address(); // game2 let addr2 = Game { counter: 0, name: String::from("Game 2"), // game1 的 recipient recipient: addr.recipient(), } .start(); // game2 先发送 addr2.do_send(Ping { id: 10 }); Game { counter: 0, name: String::from("Game 1"), recipient: addr2.recipient(), } }); }); system.run(); }
Actor Arbiter
Arbiter
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let sys = System::new(); let exec = async { TheActor.start(); }; // 使用Arbiter管理Actor let arbiter = Arbiter::new(); Arbiter::spawn(&arbiter, exec); System::current().stop(); sys.run(); }
SyncArbiter
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { use actix::prelude::*; struct MySyncActor; impl Actor for MySyncActor { type Context = SyncContext<Self>; } // 线程数2则可以有同时两个Actor在处理 let addr = SyncArbiter::start(2, || MySyncActor); }
Rust Low-level(Async,Syntax,)
syn,quote
quote
This crate provides the quote! macro for turning Rust syntax tree data structures into tokens of source code. The idea of quasi-quoting is that we write code that we treat as data.
基本类型
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let u = 12usize; let i = -38i32; let f = 3.1415926f64; let c = '\r'; let s = "\r\nhello\tworld\r\n"; assert_eq!( "12usize - 38i32 3.1415926f64 '\\r' \"\\r\\nhello\\tworld\\r\\n\"", quote! { u #i #f #c #s } .to_string() ); macro_rules! m { ($literal:literal) => { quote!($literal) }; } let expected = "- false"; assert_eq!(expected, m!(-false).to_string()); }
重复、循环
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let f0 = format_ident!("World"); let f1 = format_ident!("Hello{x}", x = f0); assert_eq!("HelloWorld",f1.to_string()); // ident not impl f64 let f2 = format_ident!("Hello{x}", x = 4050usize); assert_eq!("Hello4050",f2.to_string()); let num: u32 = 10; let octal = format_ident!("Id_{:o}", num); assert_eq!(octal, "Id_12"); let binary = format_ident!("Id_{:b}", num); assert_eq!(binary, "Id_1010"); let lower_hex = format_ident!("Id_{:x}", num); assert_eq!(lower_hex, "Id_a"); let upper_hex = format_ident!("Id_{:X}", num); assert_eq!(upper_hex, "Id_A"); }
注释
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let token1 = quote!{ /* comment */ }; let token2 = quote!{ // comment }; assert_eq!(token1.to_string(),token2.to_string()) }
syn
Syn is a parsing library for parsing a stream of Rust tokens into a syntax tree of Rust source code.
syn::File
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { let mut file = File::open(&filename).expect("Unable to open file"); let mut src = String::new(); file.read_to_string(&mut src).expect("Unable to read file"); let ast = syn::parse_file(&src).unwrap(); if let Some(shebang) = ast.shebang { println!("{}", shebang); } println!("{} items", ast.items.len()); }
DeriveInput for proc_macro_derive
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { #[proc_macro_derive(HeapSize)] pub fn derive_heap_size(input: proc_macro::TokenStream) -> proc_macro::TokenStream { // Parse the input tokens into a syntax tree. let input = parse_macro_input!(input as DeriveInput); // Used in the quasi-quotation below as `#name`. let name = input.ident; // Add a bound `T: HeapSize` to every type parameter T. let generics = add_trait_bounds(input.generics); let (impl_generics, ty_generics, where_clause) = generics.split_for_impl(); // Generate an expression to sum up the heap size of each field. let sum = heap_size_sum(&input.data); let expanded = quote! { // The generated impl. ... }; // Hand the output tokens back to the compiler. proc_macro::TokenStream::from(expanded) } }
fold 可以在语法转换时hook
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { impl Fold for Args { // 处理expr类型时 fn fold_expr(&mut self, e: Expr) -> Expr { match e { Expr::Assign(e) => { if self.should_print_expr(&e.left) { self.assign_and_print(*e.left, &e.eq_token, *e.right) } else { Expr::Assign(fold::fold_expr_assign(self, e)) } } Expr::Binary(e) if is_assign_op(e.op) => { if self.should_print_expr(&e.left) { self.assign_and_print(*e.left, &e.op, *e.right) } else { Expr::Binary(fold::fold_expr_binary(self, e)) } } _ => fold::fold_expr(self, e), } } // 处理stmt类型 fn fold_stmt(&mut self, s: Stmt) -> Stmt { match s { Stmt::Local(s) => { if s.init.is_some() && self.should_print_pat(&s.pat) { self.let_and_print(s) } else { Stmt::Local(fold::fold_local(self, s)) } } _ => fold::fold_stmt(self, s), } } } }
serde
Serde is a framework for serializing and deserializing Rust data structures efficiently and generically.
仅依赖syn ,quote ,proc-macro2
基本操作
use serde::{Deserialize, Serialize}; // 主要是 Serialize,Deserialize 这两个宏 #[derive(Serialize, Deserialize, Debug)] struct Point { x: i32, y: i32, } fn main() { let point = Point { x: 1, y: 2 }; // Convert the Point to a JSON string. let serialized = serde_json::to_string(&point).unwrap(); // Prints serialized = {"x":1,"y":2} println!("serialized = {}", serialized); // Convert the JSON string back to a Point. let deserialized: Point = serde_json::from_str(&serialized).unwrap(); // Prints deserialized = Point { x: 1, y: 2 } println!("deserialized = {:?}", deserialized); }
Deserialize
#![allow(unused)] fn main() { // 以该结构为例子 #[derive(Serialize,Debug)] struct Duration{ secs:usize, nanos:usize, } // 方便反序列化 impl Duration { fn new(secs:usize,nanos:usize) -> Duration{ return Duration { secs:secs, nanos:nanos, } } } // 实现反序列化 impl<'de> Deserialize<'de> for Duration { fn deserialize<D>(deserializer: D) -> Result<Self, D::Error> where D: Deserializer<'de>, { enum Field { Secs, Nanos } // This part could also be generated independently by: // // #[derive(Deserialize)] // #[serde(field_identifier, rename_all = "lowercase")] // enum Field { Secs, Nanos } // 给每个字段实现反序列化 impl<'de> Deserialize<'de> for Field { fn deserialize<D>(deserializer: D) -> Result<Field, D::Error> where D: Deserializer<'de>, { struct FieldVisitor; // visitor用于处理基本类型 impl<'de> Visitor<'de> for FieldVisitor { type Value = Field; fn expecting(&self, formatter: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result { formatter.write_str("`secs` or `nanos`") } fn visit_str<E>(self, value: &str) -> Result<Field, E> where E: de::Error, { match value { "secs" => Ok(Field::Secs), "nanos" => Ok(Field::Nanos), _ => Err(de::Error::unknown_field(value, FIELDS)), } } } // 处理字段名 deserializer.deserialize_identifier(FieldVisitor) } } struct DurationVisitor; impl<'de> Visitor<'de> for DurationVisitor { type Value = Duration; fn expecting(&self, formatter: &mut fmt::Formatter) -> fmt::Result { formatter.write_str("struct Duration") } // 针对序列 fn visit_seq<V>(self, mut seq: V) -> Result<Duration, V::Error> where V: SeqAccess<'de>, { let secs = seq.next_element()? .ok_or_else(|| de::Error::invalid_length(0, &self))?; let nanos = seq.next_element()? .ok_or_else(|| de::Error::invalid_length(1, &self))?; Ok(Duration::new(secs, nanos)) } // 常见的反序列化map fn visit_map<V>(self, mut map: V) -> Result<Duration, V::Error> where V: MapAccess<'de>, { let mut secs = None; let mut nanos = None; while let Some(key) = map.next_key()? { match key { Field::Secs => { if secs.is_some() { return Err(de::Error::duplicate_field("secs")); } secs = Some(map.next_value()?); } Field::Nanos => { if nanos.is_some() { return Err(de::Error::duplicate_field("nanos")); } nanos = Some(map.next_value()?); } } } let secs = secs.ok_or_else(|| de::Error::missing_field("secs"))?; let nanos = nanos.ok_or_else(|| de::Error::missing_field("nanos"))?; Ok(Duration::new(secs, nanos)) } } const FIELDS: &'static [&'static str] = &["secs", "nanos"]; deserializer.deserialize_struct("Duration", FIELDS, DurationVisitor) } } // 最后测试 let d = Duration{secs:123,nanos:345}; let ds = serde_json::to_string(&d).unwrap(); println!("{}",ds); let dd:Duration = serde_json::from_str(&ds).unwrap(); println!("{:#?}",dd); }
Java Low-level(Native,VirtualThread,FFM)
ScopedValue,StructuredTaskScope
JEP 429: Scoped Values (Incubator) 代码用的java版本是 openjdk 22-internal ,SOURCE=".:git:ad34be1f329e"
基本用法
isBound, get
// get
ScopedValue<String> name = ScopedValue.newInstance();
String result = ScopedValue.getWhere(name, "duke", ()->{
// 在这个scope里是inbound的
System.out.println(name.isBound());
// 所以这个scope里才能get到值
return name.get();
});
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println(name.isBound());
几个开启scope的方法runWhere,callWhere,getWhere
ScopedValue<String> v1 = ScopedValue.newInstance();
ScopedValue.runWhere(v1,"new v1 run",()->{
System.out.println(v1.get());
});
ScopedValue.callWhere(v1,"new v1 call",()->{
System.out.println(v1.get());
return v1.get();
});
ScopedValue.getWhere(v1,"new v1 get",() ->{
System.out.println(v1.get());
return v1.get();
});
assert "default" == v1.orElse("default");
ScopedValue.runWhere(v1,"the",()->{
assert "the" == v1.orElse(null);
});
scope嵌套
ScopedValue<String> v1 = ScopedValue.newInstance();
ScopedValue.runWhere(v1,"v1 leve1",()->{
assert v1.isBound();
assert "v1 leve1" == v1.get();
ScopedValue.runWhere(v1,"v1 leve2",()->{
assert v1.isBound();
assert "v1 leve2" == v1.get();
});
assert v1.isBound();
assert "v1 leve1" == v1.get();
});
多值
ScopedValue<String> name = ScopedValue.newInstance();
ScopedValue<Integer> age = ScopedValue.newInstance();
ScopedValue.where(name,"my name")
.where(age,22)
.run(()->{
assert name.isBound();
assert age.isBound();
System.out.println(name.get());
System.out.println(age.get());
});
StructuredTaskScope 的PreviewFeature的版本,与19release的版本略有不同
对了 如果一些没有relase的版本的代码片段在IDEA上无法运行,就直接java XXX 吧,java已经可以直接执行java文件了, 加上
--enable-preview --source 22即可
fork with virtual thread
Set<Thread> threads = ConcurrentHashMap.newKeySet();
try (var scope = new StructuredTaskScope<Object>("v",
// 通过虚拟线程创建100个fork非常快
Thread.ofVirtual().factory())) {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
scope.fork(() -> {
threads.add(Thread.currentThread());
return null;
});
}
scope.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
assert 100 == threads.size();
assert 100 == threads.stream().filter(t->t.isVirtual()).count();
ShutdownOnSuccess
// 源码处
if (subtask.state() == Subtask.State.SUCCESS) {
// task succeeded
T result = subtask.get();
Object r = (result != null) ? result : RESULT_NULL;
if (FIRST_RESULT.compareAndSet(this, null, r)) {
// 确认是第一个成功的就shutdown
super.shutdown();
}
}
// 比如
try(var scope = new StructuredTaskScope.ShutdownOnSuccess<>()) {
StructuredTaskScope.Subtask<Object> f1 = scope.fork(()->{
return "1";
});
StructuredTaskScope.Subtask<Object> f2 = scope.fork(()->{
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
return "2";
});
System.out.println(f1.state());
System.out.println(f2.state());
scope.join();
System.out.println("join");
System.out.println(f1.state());
System.out.println(f2.state());
// get会报错,因为其中一个成功后其他的已经取消了
// System.out.println(f1.get());
// System.out.println(f2.get());
System.out.println(scope.result());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (ExecutionException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
自定义scope handle
public static class MyScopeException extends RuntimeException {}
public static class MyScope extends StructuredTaskScope<String> {
private final Collection<String> oks = new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<>();
private final Collection<Throwable> errs = new ConcurrentLinkedDeque<>();
@Override
protected void handleComplete(Subtask<? extends String> subtask) {
switch (subtask.state()){
case UNAVAILABLE : throw new IllegalStateException("");
case SUCCESS : this.oks.add(subtask.get());break;
case FAILED : this.errs.add(subtask.exception());break;
default : {}break;
}
}
public MyScopeException errors(){
MyScopeException exception = new MyScopeException();
errs.forEach(exception::addSuppressed);
return exception;
}
public String myResult(){
return oks.stream().findFirst().orElseThrow(this::errors);
}
}
使用自定义的scope
try(var scope = new MyScope()) {
scope.fork(()->{
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
return "1";
});
scope.fork(()->{
return "2";
});
scope.join();
System.out.println(scope.myResult());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
FFM(Foreign Function & Memory)
可以调用外部的函数比如,native的lib中的函数
外部函数调用,以naitve的stdlib中的函数为例
// strlen
Linker linker = abi.nativeLinker();
MethodHandle strlen = abi.downcallHandle(
abi.defaultLookup().find("strlen").orElseThrow(),
// 返回值 是 long 参数是地址
FunctionDescriptor.of(JAVA_LONG, ADDRESS)
);
try (Arena arena = Arena.ofConfined()) {
// 创建Hello的char[]这种值
MemorySegment str = arena.allocateUtf8String("Hello");
long len = (long) strlen.invokeExact(str); // 5
System.out.println(len);
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// qsrot 参数是array 返回值也是array
final AddressLayout C_POINTER = ADDRESS
.withTargetLayout(MemoryLayout.sequenceLayout(JAVA_BYTE));
// qsort函数
MethodHandle qsort = abi.downcallHandle(abi.defaultLookup().find("qsort").get(),
FunctionDescriptor.ofVoid(C_POINTER, JAVA_LONG, JAVA_LONG, C_POINTER));
FunctionDescriptor qsortComparFunction = FunctionDescriptor.of(JAVA_INT,
C_POINTER.withTargetLayout(JAVA_INT), C_POINTER.withTargetLayout(JAVA_INT));
MethodHandle qsortCompar = MethodHandles.lookup().findStatic(
Demo1.class,"qsortCompare",qsortComparFunction.toMethodType()
);
int[] arr = new int[]{4,3,2,1,4,3};
//init native array
try (var arena = Arena.ofConfined()) {
MemorySegment nativeArr = arena.allocateArray(JAVA_INT, arr);
//call qsort
MemorySegment qsortUpcallStub = abi.upcallStub(qsortCompar, qsortComparFunction, arena);
qsort.invokeExact(nativeArr, (long)arr.length, JAVA_INT.byteSize(), qsortUpcallStub);
//convert back to Java array
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nativeArr.toArray(JAVA_INT)));
} catch (Throwable e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
内存操作
基本的值类型
MemoryLayout seq = MemoryLayout.sequenceLayout(10, ValueLayout.JAVA_INT);
try (Arena arena = Arena.ofConfined()) {
MemorySegment segment = arena.allocate(seq);;
VarHandle indexHandle = seq.varHandle(MemoryLayout.PathElement.sequenceElement());
// init segment
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) {
indexHandle.set(segment, (long)i, i);
}
//check statically indexed handles
for (int i = 0 ; i < 10 ; i++) {
VarHandle preindexHandle = seq.varHandle(MemoryLayout.PathElement.sequenceElement(i));
int expected = (int)indexHandle.get(segment, (long)i);
int found = (int)preindexHandle.get(segment);
assert expected == found;
}
}
// slice
VarHandle byteHandle = ValueLayout.JAVA_BYTE.arrayElementVarHandle();
try (Arena arena = Arena.ofConfined()) {
MemorySegment segment = arena.allocate(10, 1);
//init
for (byte i = 0 ; i < segment.byteSize() ; i++) {
byteHandle.set(segment, (long)i, i);
}
for (int offset = 0 ; offset < 10 ; offset++) {
MemorySegment slice = segment.asSlice(offset);
for (long i = offset ; i < 10 ; i++) {
assert byteHandle.get(segment, i) == byteHandle.get(slice, i - offset);
}
}
}
Qt -
Qt - Base
Compose
https://www.jetbrains.com/zh-cn/lp/compose-multiplatform/
Compose 基本语法
启动入口
/*
main函数运行
*/
fun main() =
//An entry point for the Compose application.
// 启动函数
application {
// window
Window(title = "first demo",
onCloseRequest = ::exitApplication,
) {
// window > 组件
App()
}
}
组件
/**
* @Composable 组件注解 给函数加上注解就代表一个页面组件
* @Preview 可以借助IDEA上的插件进行组件预览
*/
@Composable
@Preview
fun App() {
// 计算 状态 当值变化并需要页面变得时会重新运行相关作用域代码的这个组件
var text by remember { mutableStateOf("Hello, World!") }
println("app scope")
MaterialTheme {
Button(onClick = {
text = "Hello, Desktop!"
}) {
println("text scope")
Text(text)
}
}
}
Idea 预览效果

Component
自定义组件
@Composable
fun MyPart(color:Color, // 属性
onClick:() -> Unit, // 事件
context:@Composable ()->Unit // 内部Context
){
Box(modifier = Modifier.background(color).padding(10.dp)
.clickable(true,onClick={
onClick()
})){
context()
}
}
// 像其他组件一样使用
@Composable
@Preview
fun App() {
var text by remember { mutableStateOf("Hello, World!") }
MaterialTheme {
// 自定义组件
MyPart(Color.Red, onClick = {
text = "my part onclick"
}){
Text(text)
}
}
}
Events
鼠标事件
@Composable
@Preview
fun DemoEvent(){
var color by remember { mutableStateOf(Color(0,0,0)) }
var text by remember { mutableStateOf("0,0") }
@OptIn(ExperimentalComposeUiApi::class)
Box(
modifier = Modifier
.wrapContentSize(Alignment.Center)
.fillMaxSize()
.background(color=color)
.onPointerEvent(PointerEventType.Move) { // 鼠标事件
// it 可以获取事件属性
val position = it.changes.first().position
color = Color(
position.x.toInt() % 256, // x 座标映射到256
position.y.toInt() % 256, // y 座标 映射到256
0)
text = "${position.x},${position.y}"
}.onPointerEvent(PointerEventType.Scroll){
println("${it.changes.first().scrollDelta.x},${it.changes.first().scrollDelta.y}")
}
){
Text(text=text)
}
}
Arrow - Mem Table Store
Arrow DataType
My Open Source Projects
| name | link |
|---|---|
| Natural language REPL | https://gitlab.com/realcpf/nl-repl or https://jihulab.com/realcpf/nl-repl |
| PongFunctionServiceFramework | https://gitlab.com/realcpf/pongfunctionserviceframework or https://jihulab.com/realcpf/pongfunctionserviceframework |
| udspong | https://gitlab.com/realcpf/udspong or https://jihulab.com/realcpf/udspong |
| udspong rust | https://gitlab.com/realcpf/rust-udspong or https://jihulab.com/realcpf/rust-udspong |
| udspong golang | https://gitlab.com/realcpf/golang-udspong or https://jihulab.com/realcpf/golang-udspong |
| pongswallow | https://gitlab.com/realcpf/pongswallow or https://jihulab.com/realcpf/pongswallow |
| cpfplace | https://gitlab.com/realcpf/cpfplace or https://jihulab.com/realcpf/cpfplace |
| wasmworker | https://gitlab.com/realcpf/wasmworker or https://jihulab.com/realcpf/wasmworker |
High concurrency task support system
maven
<dependency>
<groupId>tech.realcpf.grape</groupId>
<artifactId>grape</artifactId>
<version>1.0.1</version>
</dependency>
图示

Process Function Call
-
send and reveice by unix domain socket
-
protocol by new simple design
-
function interface schema by functional think

Protocol Translator
一个应用层协议翻译器
第一版
- 在各个协议的decode的handler后添加转发
- 通过配置实现动态给pipline添加handler
第二版
- 构建soft的decode实现在尽可能取得需要的字段的情况下兼容多种协议

Natural language REPL
一个自然语言执行器,可以在后端支持的情况下,通过自然语言执行逻辑程序
架构图解

PongFunctionServiceFramework
设计介绍
在同一个Linux Host上的不同Container作为不同的函数进程
在这些Container直接采用Unix Domain Socket或者其他base Linux 内核的通信方式进行消息交换
对于外部网络通过一个统一的Exchange的Container进行处理与交换
Host内部提供一个Func-Router的Container作为路由对外部请求进行转发到不同的Func的Container
提供State-Conf-Center对于各个组件的Container进行统一的Func分发和状态、配置管理
而Router和各个Func的Container直接交换的是什么呢?
含义是逻辑函数,载体是DSL或者WASM二进制流
各个Func如何执行这些DSL、WASM呢?
通过Func的配置中心进行函数预加载,然后通过逻辑函数进行实际调用

udsPong
introduction
-
An inter-container messaging mechanism that does not require a TCPIP network. The underlying protocol is Unix DomainSocket, The non-blocking threading model relies on the Netty Event Loop, The message plan has a simple structure that is customized. Fast and efficient analysis, Meet the needs of KV storage, direct forwarding and other features.
-
Implementation brief: Unsafe access native Epoll ctl as the primary non-blocking support, Epoll's EPOLLIN,EPOLLOUT,EPOLLRDHUP,EPOLLET,EPOLLERR is supported
-
Message specification
1-2 3-6 7-bodylen type num(u16) body len (u32) bytes -
KV storage support:
Extend Java memory through mmap to improve access efficiency. Supports per-block compression to reduce storage pressure. Support setting cache to optimize IO pressure.
介绍
-
一种无需TCPIP网络的容器间的消息传递机制。 基础protocol是Unix DomainSocket, 非阻塞线程模型依赖Netty Event Loop, 消息规划采用自定义的简单结构, 解析迅速,高效, 满足kv存储,直接转发等多种feature。
-
实现简介: 采用Unsafe 接入native Epoll ctl 作为主要的非阻塞支持, 支持了Epoll的EPOLLIN,EPOLLOUT,EPOLLRDHUP,EPOLLET,EPOLLERR
-
消息规范
1-2 3-6 7-bodylen type num(u16) body len (u32) bytes -
kv存储支持:
通过mmap扩展java外存,提高存取效率。 支持按块压缩,降低存储压力。 支持设置缓存,优化io压力。
contact
realcpf@163.com
dev log
unix domain socket message exchanger
function list(2023/02/27)
- kv message rev and store
- kv message get from store and memory
- client register on server
- client send message by server (route by client channel name)
Scheme
- find key and end key, then slice
- fixed type key and body len,then read by len
other is coming soon!
pongswallow
介绍
-
一种在可用的程度上部分替代目前主流的线程模型实现的线程池优化实现。
初步的目标是在udsPong替代disruptor
-
通过排序算法获取灵感
基础的排序算法有这样几类,交换、归并、选择,插入。
而为了应对更具特点的数据,目前的排序算法比如22年的glidesort 以及它参考的pdqsort
都有根据数据特点划分不同的排序task,排序算法的数据称之为run
我借鉴了run这样的概念,通过手动讲复杂任务分解成为可在多个run同时执行的函数,
配合队列概念,实现有限线程数下的效率提升。
-
核心伪代码
while(worker = queue.poll() != null) { runAsync(woker.work()) .whenComplete((cworker)=>{ if(cworker.notdone()){ queue.push(worker) } }) } -
worker & run
worker 是执行的主体,每次work都会调用一个或多个的run,
而如何划分run的batch就是需要手动设计的要点
introduction
-
A thread pool optimization implementation that partially replaces the current mainstream threading model implementation to the extent available.
The initial goal is to replace disruptor in udsPong
-
Get inspired by sorting algorithms
The basic sorting algorithms have the following categories, exchange, merge, selection, insertion.
In order to cope with more characteristic data, current sorting algorithms such as 22 years of glidesort and its reference PDQSORT
There are different sorting tasks according to the characteristics of the data, and the data of the sorting algorithm is called run
I borrowed the concept of run, by manually decomposing complex tasks into functions that can be executed simultaneously by multiple runs.
With the concept of queuing, efficiency improvement under a limited number of threads is realized.
-
Core pseudocode
while(worker = queue.poll() != null) { runAsync(woker.work()) .whenComplete((cworker)=>{ if(cworker.notdone()){ queue.push(worker) } }) }
contact
realcpf@163.com
pongstore
it come from udspong's file sotre
wasmworker
use brower run wasm file as a worker
example of run wasm task with brower worker
-
load wasm by url -> go wasm example
-
test page
Dev Things
一些关于计算机开发相关的思考
PongFunctionServiceFramework
Write Before All Start
This is a new architectural paradigm
在同一个Linux Host上的不同Container作为不同的函数进程
在这些Container直接采用Unix Domain Socket或者其他base Linux 内核的通信方式进行消息交换
对于外部网络通过一个统一的Exchange的Container进行处理与交换
Host内部提供一个Func-Router的Container作为路由对外部请求进行转发到不同的Func的Container
提供State-Conf-Center对于各个组件的Container进行统一的Func分发和状态、配置管理
而Router和各个Func的Container直接交换的是什么呢?
含义是逻辑函数,载体是DSL或者WASM二进制流
各个Func如何执行这些DSL、WASM呢?
通过Func的配置中心进行函数预加载,然后通过逻辑函数进行实际调用

最后更新:2023年4月16日
Store
Raw vs column
现实世界的二维数据普遍是行展示
作为一种直观、高可读的数据展示方式
长久的应用在工作生活之中
Excel就算其一种影响极大的例子
而列存储又是怎样的呢?
在磁盘寻址的基本逻辑下
行存储将一行一行的数据连续的写入磁盘
然后
出于查询优化、降低IO等目的
采用列的排布
在每个磁盘块上写入每个字段的值
当然有着无法修改的问题
但同等字段数量的查询有着明显的提升
async , sync ,block ,non block
目前有reactor、peactor
以及终极的actor
下面是我个人的一种简单的异步分治模型
参照排序算法的多run的模型
对可分解的耗时IO任务进行拆分
每个独立的子任务
称之为run
而一个worker每次work()可以运行一个或多个run
未完成的worker继续push回queue
反复迭代
while(worker = queue.poll() != null) {
runAsync(woker.work())
.whenComplete((cworker)=>{
if(cworker.notdone()){
queue.push(worker)
}
})
}
About